Publications
2025
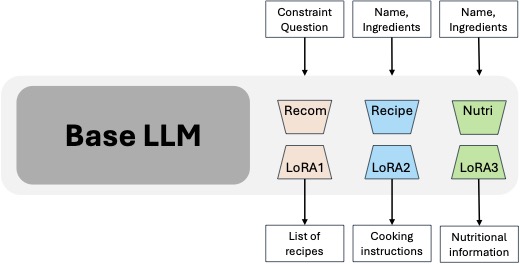 KERL: Knowledge-Enhanced Personalized Recipe Recommendation using Large Language ModelsFnu Mohbat, and Mohammed J. ZakiProceedings of the 63rd Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2025
KERL: Knowledge-Enhanced Personalized Recipe Recommendation using Large Language ModelsFnu Mohbat, and Mohammed J. ZakiProceedings of the 63rd Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2025Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) and the abundance of food data have resulted in studies to improve food understanding using LLMs. Despite several recommendation systems utilizing LLMs and Knowledge Graphs (KGs), there has been limited research on integrating food related KGs with LLMs. We introduce KERL, a unified system that leverages food KGs and LLMs to provide personalized food recommendations and generates recipes with associated micro-nutritional information. Given a natural language question, KERL extracts entities, retrieves subgraphs from the KG, which are then fed into the LLM as context to select the recipes that satisfy the constraints. Next, our system generates the cooking steps and nutritional information for each recipe. To evaluate our approach, we also develop a benchmark dataset by curating recipe related questions, combined with constraints and personal preferences. Through extensive experiments, we show that our proposed KG-augmented LLM significantly outperforms existing approaches, offering a complete and coherent solution for food recommendation, recipe generation, and nutritional analysis.
@article{mohbat-acl-25, title = {KERL: Knowledge-Enhanced Personalized Recipe Recommendation using Large Language Models}, author = {Mohbat, Fnu and Zaki, Mohammed J.}, journal = {Proceedings of the 63rd Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL)}, pages = {}, year = {2025}, publisher = {ACL}, doi = { }, }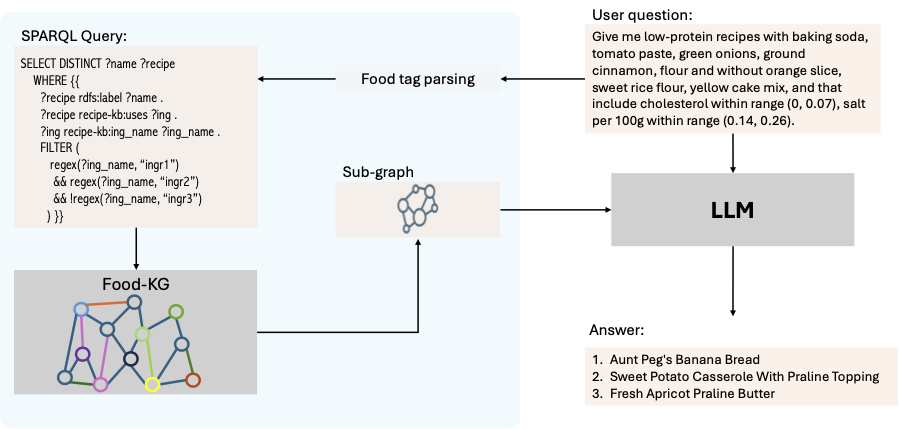 Knowledge Graph-Enhanced LLM for Food Recommendation through Question AnsweringFnu Mohbat, and Mohammed J. ZakiTowards Knowledgeable Foundation Models (KnowFM) at AAAI, 2025
Knowledge Graph-Enhanced LLM for Food Recommendation through Question AnsweringFnu Mohbat, and Mohammed J. ZakiTowards Knowledgeable Foundation Models (KnowFM) at AAAI, 2025The rich online sources of food data has resulted in creation of structured food knowledge graphs (FoodKGs) which have been applied to various food computing tasks including food recommendation. The recent advancement in large language models (LLMs) have also led to their applications in recommendation systems. Despite several food recommendation systems utilizing KGs, there is limited research on employing FoodKGs to enhance LLMs for food recommendation. We propose food recommendation as question answer over a large food knowledge graph by leveraging the power of LLMs. Given a natural language question, the system extract entities and retrieves subgraphs from the KG which are fed into the LLM as context. The LLM then selects the recipes that satisfy all the constraints in the question. In our approach we fine-tune the LLM model to take in a question and the relevant subgraph from a FoodKG, to recommends relevant recipes. We also develop a benchmark dataset by curating recipe related questions, combined with constraints and personal preferences. We show via extensive comparison that our proposed LLM plus KG model significantly outperforms the other state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLM models for food recommendation.
@article{mohbat-knowfm-25, title = {Knowledge Graph-Enhanced LLM for Food Recommendation through Question Answering}, author = {Mohbat, Fnu and Zaki, Mohammed J.}, journal = {Towards Knowledgeable Foundation Models (KnowFM) at AAAI}, year = {2025}, publisher = {AAAI}, } Neurosymbolic Methods for Food ComputingGjorgjina Cenikj, Mauro Dragoni, Tome Eftimov , and 6 more authorsHandbook on Neurosymbolic AI and Knowledge Graphs, 2025
Neurosymbolic Methods for Food ComputingGjorgjina Cenikj, Mauro Dragoni, Tome Eftimov , and 6 more authorsHandbook on Neurosymbolic AI and Knowledge Graphs, 2025In this chapter, we explore the integration of symbolic reasoning and neural network-based methods within the domain of food science. We provide a comprehensive overview of symbolic methods such as food ontologies, knowledge graphs, and their construction, emphasizing their role in enhancing data interoperability and supporting complex food computing tasks. We then discuss neural network-based techniques for extracting food information from textual and image data, food representation learning through embeddings, and present various methodologies for food category classification, nutrition estimation, and ingredient substitution. Practical applications such as personalized nutrition, dietary management, food logging, and recipe creation using generative AI are also discussed, showcasing the transformative impact of neurosymbolic methods in food computing.
@article{mohbat-neurosym-25, title = {Neurosymbolic Methods for Food Computing}, author = {Cenikj, Gjorgjina and Dragoni, Mauro and Eftimov, Tome and Koroušić Seljak, Barbara and Ławrynowicz, Agnieszka and Mohbat, Fnu and Seneviratne, Oshani and Yamakata, Yoko and Zaki, Mohammed J.}, journal = {Handbook on Neurosymbolic AI and Knowledge Graphs}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IOS Press - Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications}, }
2024
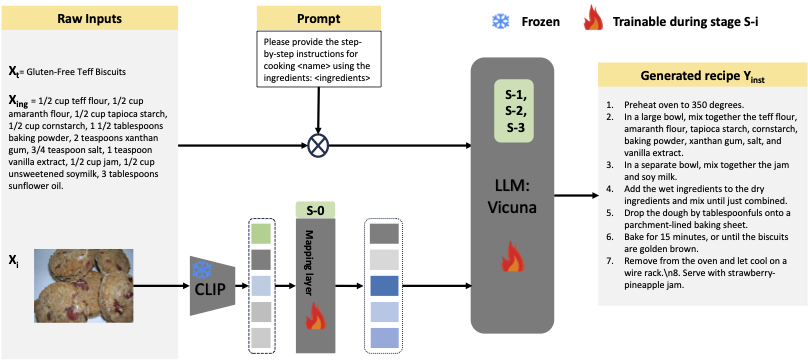 LLaVA-Chef: A Multi-modal Generative Model for Food RecipesFnu Mohbat, and Mohammed J. ZakiProceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2024
LLaVA-Chef: A Multi-modal Generative Model for Food RecipesFnu Mohbat, and Mohammed J. ZakiProceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2024In the rapidly evolving landscape of online recipe sharing within a globalized context, there has been a notable surge in research towards comprehending and generating food recipes. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) like GPT-2 and LLaVA have paved the way for Natural Language Processing (NLP) approaches to delve deeper into various facets of food-related tasks, encompassing ingredient recognition and comprehensive recipe generation. Despite impressive performance and multi-modal adaptability of LLMs, domain-specific training remains paramount for their effective application. This work evaluates existing LLMs for recipe generation and proposes LLaVA-Chef, a novel model trained on a curated dataset of diverse recipe prompts in a multi-stage approach. First, we refine the mapping of visual food image embeddings to the language space. Second, we adapt LLaVA to the food domain by fine-tuning it on relevant recipe data. Third, we utilize diverse prompts to enhance the model’s recipe comprehension. Finally, we improve the linguistic quality of generated recipes by penalizing the model with a custom loss function. LLaVA-Chef demonstrates impressive improvements over pretrained LLMs and prior works. A detailed qualitative analysis reveals that LLaVA-Chef generates more detailed recipes with precise ingredient mentions, compared to existing approaches.
@article{mohbat-cikm-24, title = {LLaVA-Chef: A Multi-modal Generative Model for Food Recipes}, author = {Mohbat, Fnu and Zaki, Mohammed J.}, journal = {Proceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM)}, pages = {1711--1721}, year = {2024}, publisher = {ACM}, doi = {10.1145/3627673.3679562}, }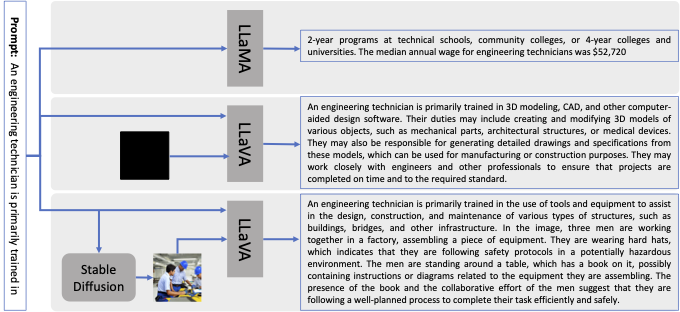 Beyond Visual Augmentation: Investigating Bias in Multi-Modal Text GenerationFnu Mohbat, Vijay Sadashivaiah, Keerthiram Murugesan , and 3 more authorsFourth Workshop on Trustworthy Natural Language Processing (TrustNLP) at NAACL, 2024
Beyond Visual Augmentation: Investigating Bias in Multi-Modal Text GenerationFnu Mohbat, Vijay Sadashivaiah, Keerthiram Murugesan , and 3 more authorsFourth Workshop on Trustworthy Natural Language Processing (TrustNLP) at NAACL, 2024The emergence of several contemporary text-to- image generation models such as DALL-E and Stable Diffusion has demonstrated remarkable proficiency in producing high-quality images. While these generated images have been used to improve text quality in natural language gen- eration (NLG) tasks via visual augmentation, parallel research endeavors have found biases within these generated images. Conversely, image-to-text models, grounded in large lan- guage models (LLMs), excel in crafting vivid descriptions of images using high-quality lan- guage, albeit inheriting the biases inherent in LLMs. This research explores how these biases are amplified when generated images are used as input for image-to-text generation models. Through empirical analysis, we show that by feeding biased images into image-to-text mod- els, the generated response becomes even more biased.
@article{mohbat-trustNLP-24, title = {Beyond Visual Augmentation: Investigating Bias in Multi-Modal Text Generation}, author = {Mohbat, Fnu and Sadashivaiah, Vijay and Murugesan, Keerthiram and Dhurandhar, Amit and Luss, Ronny and Chen, Pin-Yu}, journal = {Fourth Workshop on Trustworthy Natural Language Processing (TrustNLP) at NAACL}, year = {2024}, publisher = {ACL}, }
2023
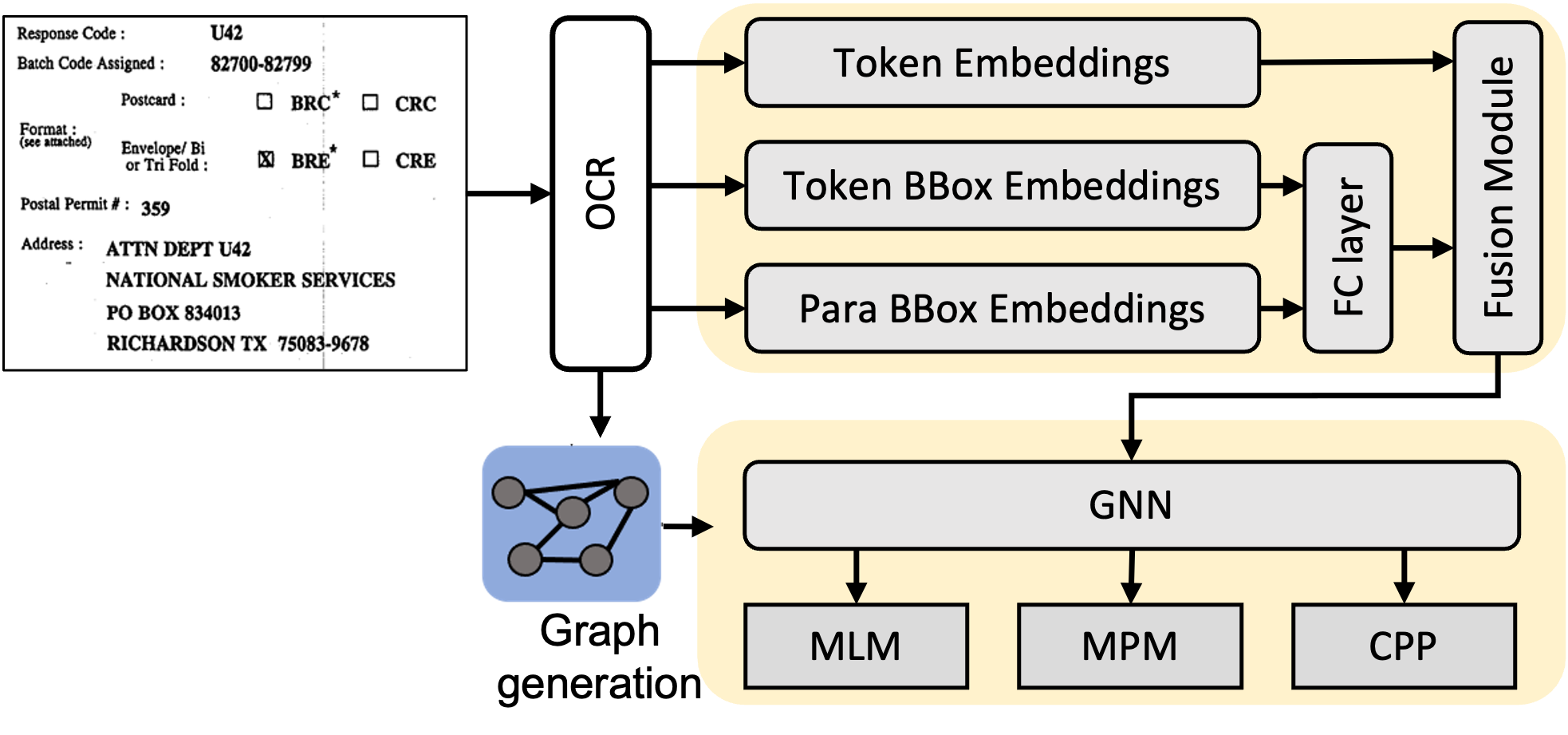 GVdoc - Graph-based Visual DOcument ClassificationFnu Mohbat, Mohammed J. Zaki, Catherine Finegan-Dollak , and 1 more authorFindings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2023
GVdoc - Graph-based Visual DOcument ClassificationFnu Mohbat, Mohammed J. Zaki, Catherine Finegan-Dollak , and 1 more authorFindings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2023The robustness of a model for real-world deployment is decided by how well it performs on unseen data and distinguishes between in-domain and out-of-domain samples. Visual document classifiers have shown impressive performance on in-distribution test sets. However, they tend to have a hard time correctly classifying and differentiating out-of-distribution examples. Image-based classifiers lack the text component, whereas multi-modality transformer-based models face the token serialization problem in visual documents due to their diverse layouts. They also require a lot of computing power during inference, making them impractical for many real-world applications. We propose, GVdoc, a graph-based document classification model that addresses both of these challenges. Our approach generates a document graph based on its layout, and then trains a graph neural network to learn node and graph embeddings. Through experiments, we show that our model, even with fewer parameters, outperforms state-of-the-art models on out-of-distribution data while retaining comparable performance on the in-distribution test set.
@article{mohbat-acl-23, title = {GVdoc - Graph-based Visual DOcument Classification}, author = {Mohbat, Fnu and Zaki, Mohammed J. and Finegan-Dollak, Catherine and Verma, Ashish Verma}, journal = {Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics}, pages = {5342--5357}, year = {2023}, publisher = {ACL}, }
2021
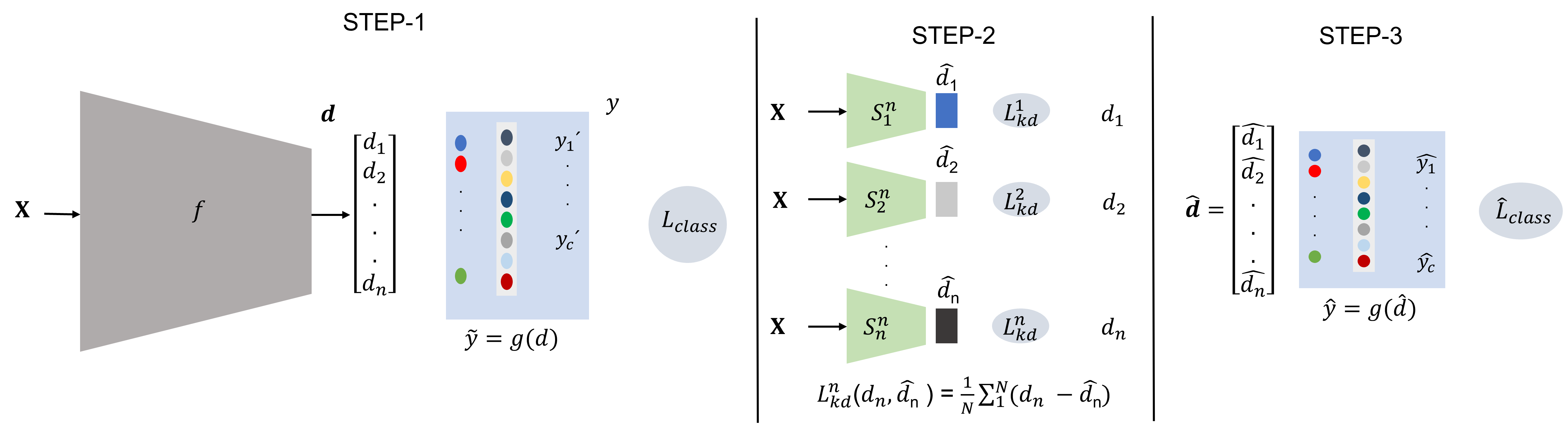 Teacher-Class Network: A Neural Network Compression MechanismShaiq Munir Malik, Muhammad Umair Haider, Mohbat Tharani , and 2 more authorsThe 32nd British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), 2021
Teacher-Class Network: A Neural Network Compression MechanismShaiq Munir Malik, Muhammad Umair Haider, Mohbat Tharani , and 2 more authorsThe 32nd British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), 2021To reduce the overwhelming size of Deep Neural Networks (DNN) teacher-student methodology tries to transfer knowledge from a complex teacher network to a simple student network. We instead propose a novel method called the teacher-class network consisting of a single teacher and multiple student networks (i.e. class of students). Instead of transferring knowledge to one student only, the proposed method transfers a chunk of knowledge to each student. Our students are not trained for problem-specific logits, they are trained to mimic knowledge (dense representation) learned by the teacher network thus the combined knowledge learned by the class of students can be used to solve other problems as well. The proposed teacher-class architecture is evaluated on several benchmark datasets such as MNIST, Fashion MNIST, IMDB Movie Reviews, CAMVid, CIFAR-10 and ImageNet on multiple tasks including image classification, sentiment classification and segmentation. Our approach outperforms the state of-the-art single student approach in terms of accuracy as well as computational cost while achieving 10-30 times reduction in parameters.
@article{bmvc-21, title = {Teacher-Class Network: A Neural Network Compression Mechanism}, author = {Malik, Shaiq Munir and Haider, Muhammad Umair and Tharani, Mohbat and Rasheed, Musab and Taj, Murtaza}, journal = {The 32nd British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC)}, year = {2021}, } Trash Detection on Water ChannelsMohbat Tharani, Abdul Wahab Amin, Fezan Rasool , and 3 more authorsInternational Conference on Neural Information Processing, 2021
Trash Detection on Water ChannelsMohbat Tharani, Abdul Wahab Amin, Fezan Rasool , and 3 more authorsInternational Conference on Neural Information Processing, 2021Rivers and canals flowing through cities are often used illegally for dumping trash that contaminates freshwater channels, causes blockage in sewerage leading to urban flooding. The dumped trash is often found floating on the water surface. We propose to automatically identify this trash through visual inspection with the eventual goal of quantification, an early warning system to avoid blockages and urban flooding. The trash could be disfigured, partially submerged, or clumped together with other objects which obscure its shape and appearance. Thus, we consider surface trash as a blob detection problem that could either be solved as object detection or image segmentation or both. To this extent, we evaluate and compare several deep-learning-based object detection and segmentation algorithms. Unlike ocean trash, to the best of our knowledge, there is no large dataset on urban trash on water channels. Thus, using IoT-based camera nodes at multiple water channels, we collected a large dataset containing 48, 450 trash objects annotated for both bounding box and segmentation (the dataset will be made publicly available (Dataset is available at https://cvlab.lums.edu.pk/watertrash/)). In addition, we also propose modifications in state-of-the-art detection and segmentation algorithms to cater to an issue such as partially submerged, varying object sizes, and edge-based computing.
@article{trash-detection-21, title = {Trash Detection on Water Channels}, author = {Tharani, Mohbat and Amin, Abdul Wahab and Rasool, Fezan and Maaz, Mohammad and Taj, Murtaza and Muhammad, Abubakar}, journal = {International Conference on Neural Information Processing}, pages = {379--389}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-92185-9_31}, year = {2021}, }
2019
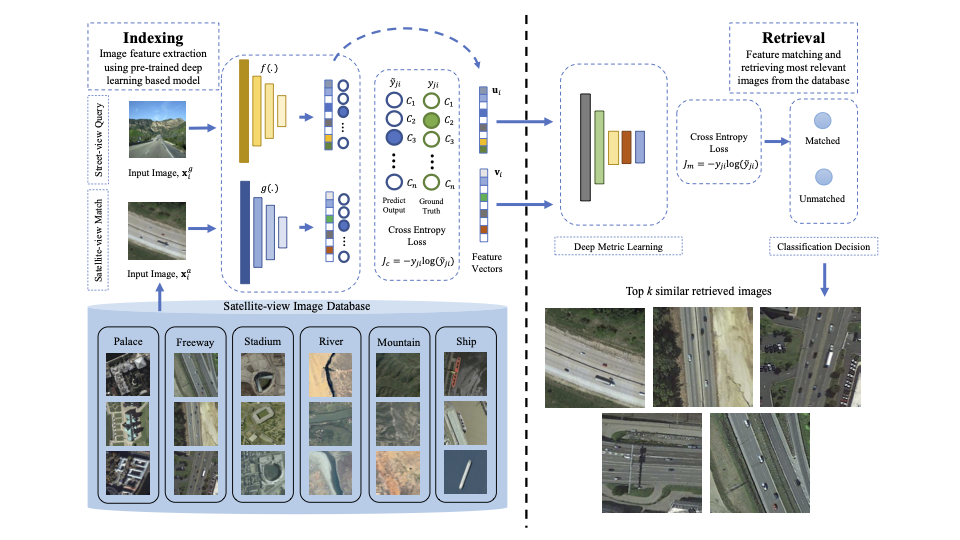 Cross-view Image Retrieval - Ground to Aerial Image Retrieval Through Deep LearningNuman Khurshid, Talha Hanif, Mohbat Tharani , and 1 more authorInternational Conference on Neural Information Processing, 2019
Cross-view Image Retrieval - Ground to Aerial Image Retrieval Through Deep LearningNuman Khurshid, Talha Hanif, Mohbat Tharani , and 1 more authorInternational Conference on Neural Information Processing, 2019Cross-modal retrieval aims to measure the content similarity between different types of data. The idea has been previously applied to visual, text, and speech data. In this paper, we present a novel cross-modal retrieval method specifically for multi-view images, called Cross-view Image Retrieval CVIR. Our approach aims to find a feature space as well as an embedding space in which samples from street-view images are compared directly to satellite-view images (and vice-versa). For this comparison, a novel deep metric learning based solution “DeepCVIR” has been proposed. Previous cross-view image datasets are deficient in that they (1) lack class information; (2) were originally collected for cross-view image geolocalization task with coupled images; (3) do not include any images from off-street locations. To train, compare, and evaluate the performance of cross-view image retrieval, we present a new 6 class cross-view image dataset termed as CrossViewRet which comprises of images including freeway, mountain, palace, river, ship, and stadium with 700 high-resolution dual-view images for each class. Results show that the proposed DeepCVIR outperforms conventional matching approaches on CVIR task for the given dataset and would also serve as the baseline for future research.
@article{iconip-19, title = {Cross-view Image Retrieval - Ground to Aerial Image Retrieval Through Deep Learning}, author = {Khurshid, Numan and Hanif, Talha and Tharani, Mohbat and Taj, Murtaza}, journal = {International Conference on Neural Information Processing}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-36711-4_19}, year = {2019}, pages = {210--221}, }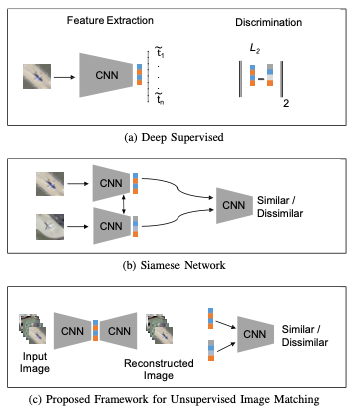 A Residual-Dyad Encoder Discriminator Network for Remote Sensing Image MatchingNuman Khurshid*, Mohbat Tharani*, Murtaza Taj , and 1 more authorIEEE Transaction on Geo-science and Remote Sensing, 2019
A Residual-Dyad Encoder Discriminator Network for Remote Sensing Image MatchingNuman Khurshid*, Mohbat Tharani*, Murtaza Taj , and 1 more authorIEEE Transaction on Geo-science and Remote Sensing, 2019We propose a new method for remote sensing image matching. The proposed method uses an encoder subnetwork of an autoencoder pretrained on the GTCrossView data to construct image features. A discriminator network trained on the University of California Merced land-use/land-cover data set (LandUse) and the high-resolution satellite scene data set (SatScene) computes a match score between a pair of computed image features. We also propose a new network unit, called residual-dyad, and empirically demonstrate that networks that use residual-dyad units outperform those that do not. We compare our approach with both traditional and more recent learning-based schemes on the LandUse and SatScene data sets, and the proposed method achieves the state-of-the-art result in terms of mean average precision and average normalized modified retrieval rank (ANMRR) metrics. Specifically, our method achieves an overall improvement in performance of 11.26% and 22.41%, respectively, for LandUse and SatScene benchmark data sets.
@article{tgrs-19, title = {A Residual-Dyad Encoder Discriminator Network for Remote Sensing Image Matching}, author = {Khurshid*, Numan and Tharani*, Mohbat and Taj, Murtaza and Qureshi, Faisal}, journal = {IEEE Transaction on Geo-science and Remote Sensing}, doi = {10.1109/TGRS.2019.2951820}, year = {2019}, }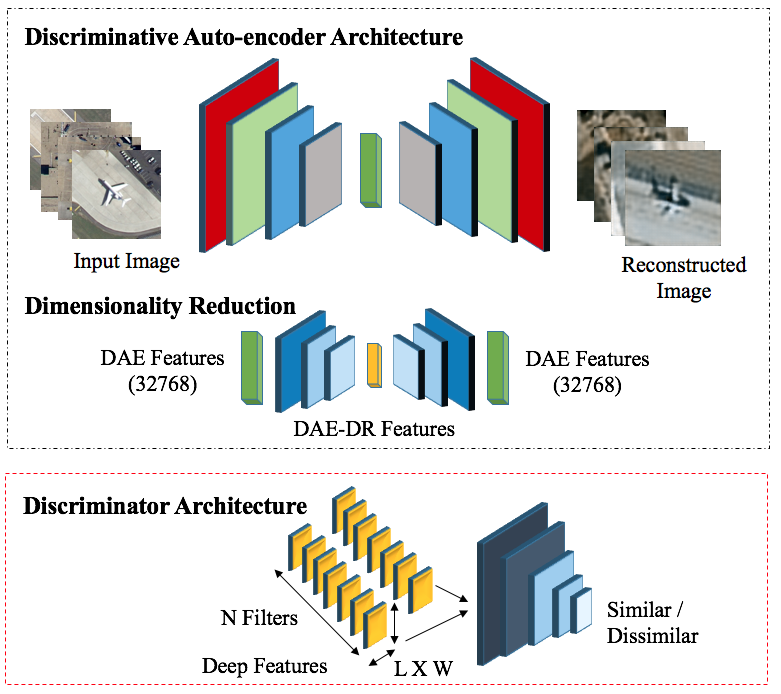 Dimensionality Reduction Using Discriminative Autoencoders for Remote Sensing Image RetrievalFnu Mohbat, Tooba Mukhtar, Numan Khurshid , and 1 more authorThe 20th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing (ICAIP), 2019
Dimensionality Reduction Using Discriminative Autoencoders for Remote Sensing Image RetrievalFnu Mohbat, Tooba Mukhtar, Numan Khurshid , and 1 more authorThe 20th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing (ICAIP), 2019Advancements in deep learning techniques caused a paradigm shift in feature extraction for image perception from handcrafted methods to deep methods. However, these deep features if learned through unsupervised methods bear large memory footprints and are prone to the curse of dimensionality. Traditional feature reduction schemes involving aggregation of these learned visual descriptors may lead to loss of essential information necessary for their obvious discrimination. Therefore, this research studies various feature reduction techniques for remote sensing image features. We also propose an deep discriminative network with dimensionality reduction (DAE-DR), exploiting stacked autoencoder based solution to abbreviate unsupervised features without significantly affecting their discriminative and regenerative characteristics. It is observed that the spatial dimensions encoded in the feature vector are more important than increasing the number of network filters for efficient image reconstruction. Validation of our approach has been tested for remote sensing image retrieval (RSIR) problem. Results demonstrate that our proposed network achieves 25 times reduction in feature size with only 0.8 times depletion of retrieval score.
@article{iciap-19, title = {Dimensionality Reduction Using Discriminative Autoencoders for Remote Sensing Image Retrieval}, author = {Mohbat, Fnu and Mukhtar, Tooba and Khurshid, Numan and Taj, Murtaza}, journal = {The 20th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing (ICAIP)}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-30642-7_45}, year = {2019}, }
2017
 Use of Greendrone UAS System for Maize Crop MonitoringAhmad Kamal Nasir, and Mohbat TharaniThe International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2017
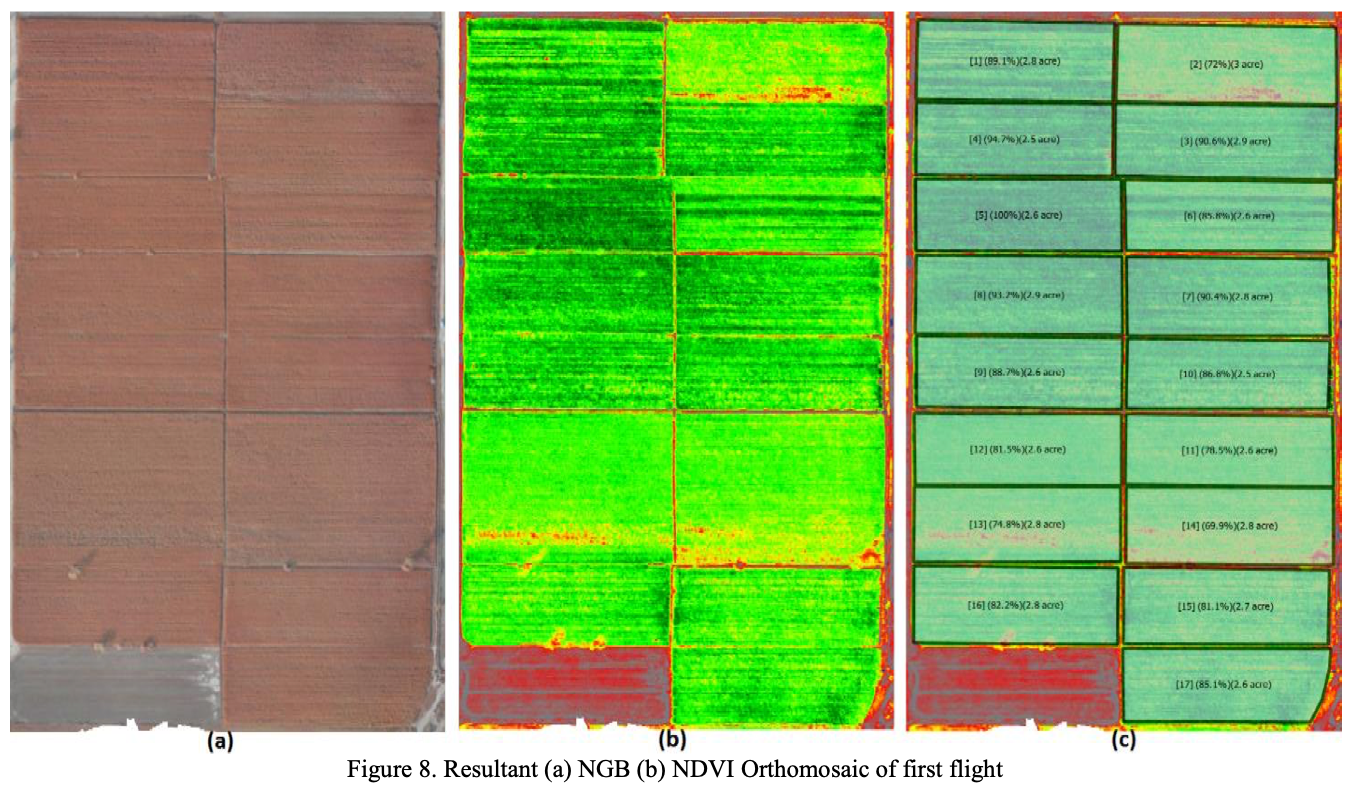
Use of Greendrone UAS System for Maize Crop MonitoringAhmad Kamal Nasir, and Mohbat TharaniThe International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2017This research work presents the use of a low-cost Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) – GreenDrone for the monitoring of Maize crop. GreenDrone consist of a long endurance fixed wing air-frame equipped with a modified Canon camera for the calculation of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and FLIR thermal camera for Water Stress Index (WSI) calculations. Several flights were conducted over the study site in order to acquire data during different phases of the crop growth. By the calculation of NDVI and NGB images we were able to identify areas with potential low yield, spatial variability in the plant counts, and irregularities in nitrogen application and water application related issues. Furthermore, some parameters which are important for the acquisition of good aerial images in order to create quality Orthomosaic image are also discussed.
@article{uas-17, title = {Use of Greendrone UAS System for Maize Crop Monitoring}, author = {Nasir, Ahmad Kamal and Tharani, Mohbat}, journal = {The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences}, doi = {10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-2-W6-263-2017}, year = {2017}, }